User Experience Questions
Questions & Answers to UX interview questions. Pull requests for suggestions and corrections are welcome!
This section is a work in progress.
Table of contents
- What is UX?*
- How does UX fit within tech?
- Why is it important to know how to code as a UX designer?
- What are some components of UX?*
- What’s a wireframe? Prototype? What are the differences?
- What is a user persona?
- What tools are you familiar with? What tools are important for a UX designer?*
- What are some of the differences between designing for desktop and mobile devices?*
- How would you define visual hierarchy?
- What are design principles? Why are they important?*
- How would you describe the basic philosophies or principles that inform your designs?
- What is emotional design? How do you emotionalize design?
- In your work, how do you practice universal design?*
- How do you make a product accessible to users with disabilities?*
- What is your process for deciding which features to add to your product?
- How do you validate or conduct usability testing on a design?*
- After product launch, how do you measure the success of a product?*
- What analytical tools, data and KPIs have you used to evaluate your previous designs?*
- How do you balance business goals with the goals of the end-user?
- What is something simple that is often overlooked in UX?
What is UX?*
User Experience is how someone feels about a product.
User Experience Design is about dictating the experience people have with a product, company, or service.
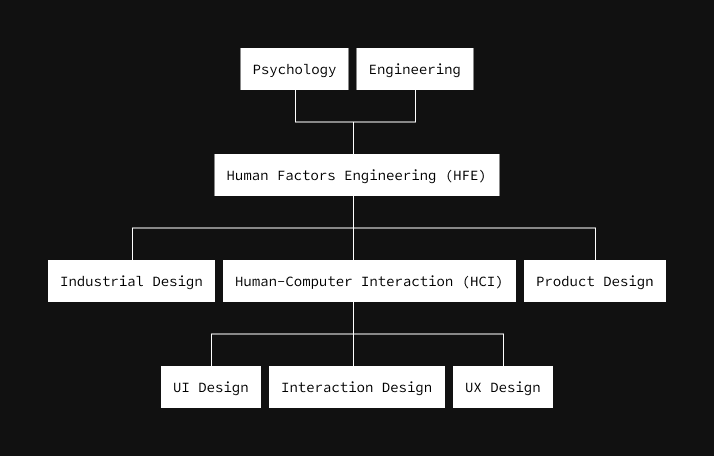
UX Design emerged as a discipline of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI). To start, the combination of Engineering and psychology formed Humans Factor Engineering (HFE), of which Industrial Design, Product Design, and HCI are subcategories. The divergence of HFE and HCI came after Cognitive Psychology became more and more influential and referenced in HCI literature and academia. Under HCI are Interaction Design, User Experience Design, and User Interface design.
HCI is about understanding how humans and computers interact whereas UX is about dictating or shaping how people experience something. But because you need to understand how users interact with computers to design good user experiences, UX falls under HCI. However, UX is becoming broader and less constrained to purely human-computer interactions.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User_experience
- https://xd.adobe.com/ideas/career-tips/what-is-ux-design/
- https://www.udacity.com/course/human-computer-interaction--ud400
How does UX fit within tech?
UX is a sub-discipline of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) that focuses on understanding how humans interact with computers. The role of a UX designer varies from company to company but generally are involved in the design and development of digital products as advocates for the end user.
Why is it important to know how to code as a UX designer?
While knowing how to code isn't necessary to be a good UX Designer, it certainly is helpful.
UX is an interdisciplinary field that requires you to work with different types of people with various types of backgrounds. As a UX designer, you'll be required to work closely with developers and engineers to implement your designs.
Knowing how to code indicates an understanding of the development process, the tools used to implement designs, and their limitations. It helps you communicate and empathize with engineers, and create designs that are considerate of the developmental resources and investment required.
If you’re not familiar with code, you might suggest designs that aren't possible, or, technically feasible but unreasonable. If designs complicate engineering requirements so much that they cannot be realized within cost and time constraints, then the design is flawed. Flawed designs create friction within the team, waste valuable time & money, and make the engineers hate you.
What are some components of UX?*
UX is a very broad field so it encompasses many subfields depending on how you define it. It has a lot of overlap with other disciplines. The main components of UX are:
- Research
- Information design & architecture
- Content Strategy
- Interaction design
- Emotional Design
- UI design
- Visual design
- Prototyping
What’s a wireframe? Prototype? What are the differences?
A wireframe is a type of prototype that demonstrates the skeleton of the design, often used to test and structure the general layout, information architecture, and relationships to other wireframes through user flows at a high level. Wireframes are used earlier in the design process and are lower fidelity.
Prototypes generally refer to a higher fidelity mock-up of the design. Prototypes are used to demonstrate the visual characteristics, interactions, and finer details of the design which means they are created further along the design process. Because prototypes are more detailed, they more closely resemble the final product design.
References
What is a user persona?
A user persona is a concise representation of an archetypal user used to align stakeholders on the type of people they are designing for.
What tools are you familiar with? What tools are important for a UX designer?
- Pen & Paper - wireframing & brainstorming
- Figma - Prototyping, component design, design systems.
- https://www.optimalworkshop.com/ - Used for card sorting and other usability tools
- https://www.typeform.com/ - Used for surveys
- https://avocode.com/ - Streamlines design-file handoffs
- https://www.protopie.io/ - Interactive Responsive Prototypes
- https://www.magicbell.com/ - Notifications
- https://www.optimizely.com/ - A/B Testing
- HTML, CSS, JS, React, DevTools, VSCode
- Browserstack
- Github
What are some of the differences between designing for desktop and mobile devices?*
The answer varies depending on the application because no standard has yet been reached. Does each have a different user interface model? What are the commonalities, and what are the differences?
There are also differences in web-development responsive design vs native mobile & desktop applications. For device-specific applications, you should refer to the device guidelines from the manufacturers and operating systems.
Summary of key differences
- Content prioritization & deferment.
- Internet Speed, data.
- Computational power, hardware, input devices (accelerometers, gyroscopes, magnetometers, proximity sensors)
- Device behavior, interaction techniques
- Navigation
- Context & Environment
- Development process
- User Expectations
References
- Julie A. Jacko. 2012. Human-Computer Interaction Handbook: Fundamentals, Evolving Technologies, and Emerging Applications, Third Edition (3rd. ed.). CRC Press, Inc., USA.
- https://developer.apple.com/design/
- https://material.io/
How would you define visual hierarchy?
Order of visual importance.
Visual hierarchy is the principle of arranging elements to show their order of importance or used to influence the perception of elements in the order you want your users to view them. It can affect how humans process information on a page. It's a system to prioritize elements so that they are easily understood.
What are design principles? Why are they important?*
Design principles are standards by which the appropriateness of the design is determined. Design principles root the design in fundamental truths. It helps guide the project and define what is subjectively right or wrong.
Design principles also align designers on common principles to follow. They may define approaches to design or guide the overall goal of the design. In this sense, design philosophies are fundamental guiding principles that dictate how a designer approaches his/her practice.
How would you describe the basic philosophies or principles that inform your designs?
It depends on the project. But generally...
- Based on real data
- Content-based design
- Appropriate
What is emotional design? How do you emotionalize design?
Emotional design is designing to elicit emotional responses from users. In Norman's emotional design, he describes three levels of emotional design:
- Visceral
- Behavioral
- Reflective
By designing for all three of these levels, you can emotionalize design.
References
- Donald A. Norman. 2004. Emotional design. Ubiquity 2004, January (January 1- January 30, 2004), 1. https://doi.org/10.1145/966012.966013
In your work, how do you practice universal design?*
- Accessibility
- Typography
- Color Contrast
- Color blindness
- Aware of Cultural Differences
- Color perception & meaning
- UI compatibility
- RTL & LTR text
- Date format
- Character limits
- Ability to change language
- WAI-ARIA
- W3 WCAG Guidelines
How do you make a product accessible to users with disabilities?*
- Follow the ARIA accessibility guidelines.
- Use tests to determine potential issues.
- Gather data and feedback.
References
What is your process for deciding which features to add to your product?
- Start with research and feedback.
- Validate and make sure its necessary or that the users even want it.
- Discuss with engineers to determine feasibility if necessary, or to get them in the discussion.
- Build a prototype.
How do you validate or conduct usability testing on a design?*
- Depends on what stage of the design.
- Wireframe testing
- Task flow analysis
- Test designs against user flows
- A/B Testing
- Watch user perform tasks
- Build prototypes
After product launch, how do you measure the success of a product?*
Identify, measure and analyze KPIs.
What analytical tools, data and KPIs have you used to evaluate your previous designs?*
Tools
- Google Analytics
- Google Lighthouse
Metrics
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP).
- First Input Delay (FID).
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
- Net promoter score (NPS). "How likely are you to recommend us to a friend?"
- Click-through rate (CTR). How many users completed steps in the golden path
- Daily active users (DAU).
- Bounce rates
- Interactivity
Pulse Framework
- Page Views
- Uptime
- Latency
- Seven-day Active users
- Earnings
HEART Framework
- Happiness: Satisfaction, NPS, Surveys. More qualitative.
- Engagement: User activity, CTR,
- Adoption - New Users, DAU, Registrations.
- Retention - % Active Over Time, Churn Rate.
- Task Success - Time, Completed tasks, Errors
References
- https://web.dev/learn-web-vitals/
- https://web.dev/vitals-business-impact/
- https://library.gv.com/how-to-choose-the-right-ux-metrics-for-your-product-5f46359ab5be
- Rodden, K., Hutchinson, H., & Fu, X. (2010, April). Measuring the user experience on a large scale: user-centered metrics for web applications. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on human factors in computing systems (pp. 2395-2398). https://research.google/pubs/pub36299/
How do you balance business goals with the goals of the end-user?
Negotiate, but ultimately it is up to the business. How to negotiate? Reframe the goals to convey business value in your decisions. Support with data.