General Questions
General questions are broad questions that may be about design, general knowledge, or your education that somehow relates to UX. Pull requests for suggestions and corrections are welcome!
Table of contents
- What is design?*
- What is the design process?*
- How would you define design thinking?*
- What is human-centered design? How is it different from user-centered design?
- What is interaction design? What are some important concepts in interaction design?*
- What is cognitive science and how does it relate to UX, UI, or HCI?
- What is color theory?
- What are agile, scrum, lean, and waterfall in the context of software development?
What is design?*
There are many definitions for design, and the definition changes depending on who you ask.
Pentak states "A dictionary definition uses the synonym plan: To design indeed means to plan, to organize... Design is essentially the opposite of chance. In ordinary conversation, when we say “it happened by design,” we mean something was planned—it did not occur just by accident."
So if design means to plan, then we can say designers are planners.
The international council on design (ICOD) defines design as "a discipline of study and practice focused on the interaction between a person — a ‘user’— and the man-made environment, taking into account aesthetic, functional, contextual, cultural and societal considerations. As a formalized discipline, design is a modern construct."
References
- Design Basics, Ninth Edition Stephen Pentak, David A. Lauer
- https://www.theicod.org/en/professional-design/what-is-design/what-is-design
What is the design process?*
There is no single definitive design process, but they generally follow a pattern of beginning with a recognition of a problem, a need for a new design, and culminating in a solution proposal.
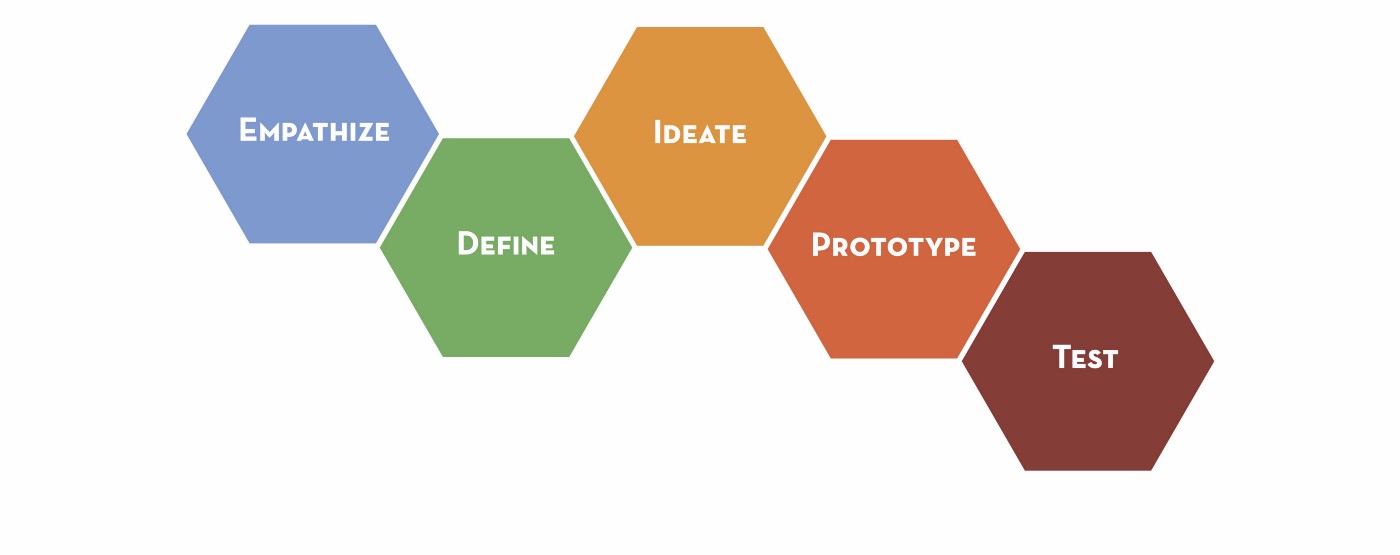
The most well-known design process is a method of design thinking popularized by Hasso Plattner Institute of Design at Stanford (d.school). The d.school design thinking method is:
- Empathize
- Define
- Ideate
- Prototype
- Test
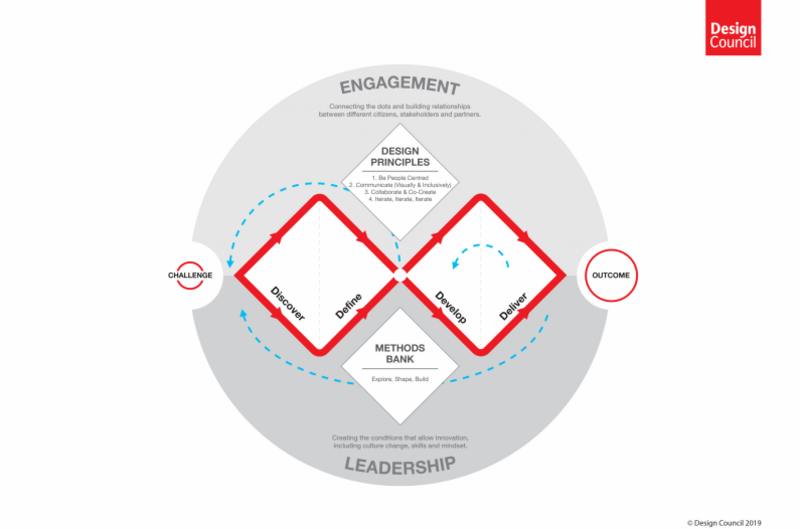
Another popular design process is The UK's Design Council Double Diamond model which describes the process in four diverging and converging phases:
- Discover (insight into the problem)
- Define (define the challenge)
- Develop (potential solutions)
- Deliver (solutions that work)
Each converging point is cyclic to model the iterative process in design.
References
- https://medium.com/stanford-d-school/lets-stop-talking-about-the-design-process-7446e52c13e8
- https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/our-work/skills-learning/tools-frameworks/framework-for-innovation-design-councils-evolved-double-diamond/
- https://designfuckingthinking.tumblr.com/
How would you define design thinking?*
Design thinking is an approach to creative problem-solving. The arts are called creative fields because there are no predetermined correct answers to the problems. Because of this, design thinking stresses the importance of understanding and correctly defining the problem to design and solve the right problem. Design thinking isn't a process or a method of design. The goal of design thinking is to let people get away from standards and processes, be innovative and solve problems with creativity.
References
- https://uxdesign.cc/is-design-thinking-a-method-of-design-no-7c7fca1ba7c6
- https://jmspool.medium.com/ssh-dont-tell-them-there-s-no-magic-in-design-thinking-b95f33867656
- https://hbr.org/2018/09/why-design-thinking-works
- https://mitsloan.mit.edu/ideas-made-to-matter/design-thinking-explained
- https://www.ideou.com/blogs/inspiration/what-is-design-thinking
What is human-centered design? How is it different from user-centered design?
Human-centered design is an approach to interactive systems development that aims to make systems usable and useful by focusing on the human aspect in all steps of the problem-solving process, their needs and requirements, and by applying human factors/ergonomics, and usability knowledge and techniques. User-centered design differs by focusing on the users and not humans as a whole.
References
What is interaction design? What are some important concepts in interaction design?*
Interaction design studies the users' behavior, their goals, and the best way to achieve them. It focuses on the communication between the user and UI, meaning, for every user input, interaction design examines how the user interface should respond - the system output.
The focus is on how people interact with technology. The goal is to enhance people's understanding of what can be done, what is happening, and what has just occurred. Interaction design draws upon principles of psychology, design, art and emotion to ensure a positive, enjoyable experience.
— Don Norman, The Design of Everyday Things, p.5
Interaction design has a lot of overlap with user experience, so a lot of familiar concepts in UX such as user flows and tasks are part of interaction design.
- Affordances & signifiers
- Discoverability
- Percepibility
- Direct manipulation
- Action-feedback loops
- Interaction cost
- Action Mapping
- User constraints
- User flow, task analysis
- Goal-driven design
- Gulf & bridge of execution & evaluation
References
- https://asktog.com/atc/principles-of-interaction-design/
- https://www.usability.gov/what-and-why/interaction-design.html
- https://boxesandarrows.com/introducing-interaction-design/
- https://www.uxbooth.com/articles/complete-beginners-guide-to-interaction-design/
- https://www.uxmatters.com/mt/archives/2007/07/what-puts-the-design-in-interaction-design.php
- https://xd.adobe.com/ideas/principles/human-computer-interaction/what-is-interaction-design/
- https://www.nngroup.com/articles/two-ux-gulfs-evaluation-execution/
What is cognitive science and how does it relate to UX, UI, or HCI?
Cognitive science is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the mind and cognition. Cognition can be thought of as a system of cognitive processes, emotion, language, memory, attention, and reasoning.
Computational Cognitive science relates computers to the brain by using them as a metaphor and as a tool used to model cognitive processes. One example of this is artificial neural networks which were modeled after biological neural nets.
To create good UX, you must understand how humans and computers interact (HCI). To understand HCI, you must understand both humans and computers. Cognitive science focuses on understanding people and their cognitive processes while my specialization in computation helps me understand computers. Bridging people and computers is the very core of what UX practitioners do.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cognitive_science
- https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/cognitive-science/
What is color theory?
Color theory is a collection of guidelines for the use of color. Some main components of color theory are:
- Additive & Subtractive Color Mixing
- Primary, Secondary, Tertiary colors
- Color in context (Color Interaction)
- Properties of colors such as:
- Hue.
- Value (light vs dark), (tint vs shade)
- Intensity aka chroma. Saturation.
- Color Wheel
References
- Design Basics, Ninth Edition Stephen Pentak, David A. Lauer
What are agile, scrum, lean, and waterfall in the context of software development?
Waterfall is a linear approach to the software development process.
Agile is an iterative approach to the software development process. Scrum and Lean are agile methods.